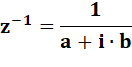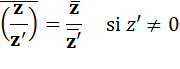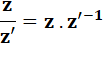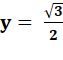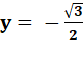|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![]()
|
Nombres complexes Conjugué et inverse |
|
|
||
|
Nombre complexe |
|
|
|
Son conjugué |
Ou noté z* en cas de
non accès au surlignement. |
|
|
Son opposé |
Pas de symbole car peu
utilisé. |
|
|
Son inverse |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Conjugué du conjugué |
|
|
|
Addition et soustraction |
|
|
|
Multiplication |
|
|
|
Conjugué d'une somme |
|
|
|
Conjugué d'un produit |
|
|
|
Conjugué d'un quotient |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
Résoudre l'équation: |
|
|
|
Passons à la forme
développée de z: |
(x
+ iy)² + (x – iy) = 0 x²
– y² + 2ixy + x – iy = 0 (x² – y² + x) + i (2xy – y) = 0 |
|
|
Rappel: |
Un nombre complexe est nul si, à la fois, sa partie réelle et sa
partie imaginaire sont nulles. |
|
|
Traitons la partie
imaginaire: |
y (2x – 1) = 0 y = 0 ou x = 1/2 |
|
|
Partie réelle |
x² + x = 0 x (x + 1) = 0 x = 0 ou x = –1
|
|
|
Partie réelle |
1/4
– y² + 1/2 = 0 y²
= 3/4
|
|
|
Les quatre solutions: |
{0, 0}, {– 1, 0}, { |
|
![]()
|
Suite |
|
|
Voir |
|
|
Cette page |
![]()