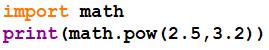|
Édition du: 28/07/2025 |
|
INDEX |
Python – Comment se lancer et initiation |
||
Faites
un double-clic pour un retour en haut de
page
![]()
|
PROGRAMMATION PYTHON – Trucs en Arithmétique Répertoire de choses à connaitre lorsqu'on
programme en Python, concernant l'arithmétique. |
||
|
|
Sommaire de cette page >>>
Nombres >>>
Factorielles et alias >>>
Constante >>>
Opérations >>>
Congruences >>>
Somme de nombres |
Débutants Glossaire |
Voir absolument Mon espace de travail en
Python
|
Nombre entier |
n = 22 / 7 print(n) print(int(n)) print(float(n)) print(f"{n:.6f}") |
3.142857142857143 3 3.142857142857143 3.142857 |
||
|
Précision au-delà de 15 décimales |
from decimal import Decimal, getcontext getcontext().prec = 30 resultat = Decimal(22) / Decimal(7) print(f"{resultat:.24f}") |
3.142857142857142857142857 |
||
|
Calcul direct avec sympy |
from sympy import Rational f = Rational(22, 7) print(f.evalf(30)) |
3.142857142857142857 \ 14285714286 |
||
|
Évaluation d'une expression |
from sympy import symbols x = symbols('x') print(int((2*x + 5).subs(x, 10).evalf())) |
25 |
||
|
Factorielle |
import math n = math.factorial(10) print(n) |
3628800 |
|
|
Et création d'un raccourci (un alias) |
import math fact = math.factorial print(fact(10)) |
3628800 |
|
|
Deux autres possibilités de création d'un alias |
def f(n): import math return math.factorial(n) print(f(10)) import math as m print(m.factorial(10)) |
3628800 3628800 |
|
|
Avec un alias pour simplifier |
import math Pi = math.pi Ex = math.exp(1) print(Pi, Ex) |
3.141592653589793 2.718281828459045 |
|
|
Division // ➔ quotient
q % ➔ reste r |
|
|
||
|
Puissance |
|
|
||
|
Puissance avec réels |
ou
|
|
||
|
Racine énième entière
d'un nombre |
from sympy import integer_nthroot def RCE(n): root, exact = integer_nthroot(n, 3) return root n = 2000 print(n, RCE(n)) |
2000 12 |
||
Rappel: comment implanter numpy et sympy dans votre logiciel Python >>>
|
Congruence |
print(100 % 7) #Cas de grands nombres print(pow(3, 95387, 10**5)) |
2 95387 |
|
Curiosité: 395387 se termine effectivement par les mêmes chiffres 95387
|
Somme des carrés pairs |
|
|||
|
Somme des pairs |
|
|
||
|
Produit des éléments d'une liste |
import math N = [2, 4, 6] P = math.prod(N) print("Produit :", P) |
Produit : 48 |
||
|
Produit de nombres dans plusieurs listes Notez le calcul de T qui réunit toutes les listes |
import math L = [ [1, 2, 3], [4], [5, 6], [], [7, 8, 9, 10] ] T = [x for S in L for x in S] print(T) somme = sum(T) produit = math.prod(T) print("Somme :", somme) print("Produit :", produit) |
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] Somme : 55 Produit : 3628800 |
||
|
Cas d'une liste complexe Utilisation d'une fonction récursive (la
fonction s'appelle elle-même) |
def extraire(data): if isinstance(data, int): return [data] elif isinstance(data, list): resultats = [] for item in data: resultats.extend(extraire(item)) return resultats else: return [] import math L = [1, [2, [3, 4], 5], [ ], [6, [7, [8]]], 9] entiers = extraire(L) somme = sum(entiers) produit = math.prod(entiers) if entiers else 0 print("Liste :", entiers) print("Somme :", somme) print("Produit :", produit) |
|
|
|
|
Liste : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] Somme : 45 Produit : 362880 |
![]()
|
Retour |
|
|
Suite |
|
|
Voir |
|
|
Sites |
|
|
Cette page |
![]()