|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![]()
|
MATRICES – Formes Diverses
matrices autour de la même matrice de départ. Matrice
transposée
Rappel: une matrice est dite carrée si elle comporte autant de lignes que de
colonnes Sinon, elle est rectangulaire. |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Matrice négative de celle d'origine. |
Matrice initiale Matrice opposée M - M |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
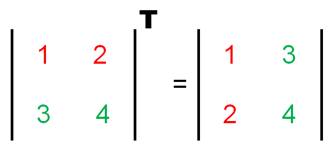
Les lignes deviennent colonnes. Les colonnes deviennent lignes. NB La transposée d'un vecteur-ligne est un
vecteur-colonne. La transposée d'un vecteur-colonne est un
vecteur-ligne. |
Matrice initiale Matrice transposée M M
T |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Décomposition en somme de matrices dont les coefficients sont tous nuls sauf celui correspondant au rang du coefficient multiplicatif de la matrice d'origine. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![]()
|
Suite |
|
|
Voir |
|
|
Cette page |
http://villemin.gerard.free.fr/Referenc/Outils/Outils/Matrice/Forme.htm |
![]()